Today we shall discus tenses and this, we know it is under
the verb series. In this case let's look at the following examples to determine
what we mean by tenses.
1. She writes this letter to please you.
2. I wrote the letter in his very presence.
3. I shall write another letter tomorrow.
In sentence 1, the Verb write refers to present time.
In sentence 2, the Verb wrote refers to past time.
In sentence 3, the Verb shall write refers to future time.
Thus a Verb may refer
(1) to present time,
(2) to past time, or
(3) to future time.
. A Verb that refers to present time is said to be present
tense. Example:
I sleep; she goes to school every day.
A verb that refers to the past or previous time is said to
be past tense. Example:
I was afraid of the beast when i saw it.
A verb that refers to the future time is said to be future
tense. Example:
I shall visit the doctor tomorrow. Hope you get it? Now
let's move on!
The Tense of a Verb shows the time of an action or event.
Note: Sometimes a past tense may refer to present time, and
a present tense may express future time, as:
I wish I knew the answer. (= I'm sorry I don't know the answer.
Past tense - Present time)
Let's wait till he comes. (Present tense - future tense)
We may now define Tense as that form of a Verb which shows
the time and the state of an action or event.
A verb agrees with its subject in number and person. Study
the verb forms of various tenses:
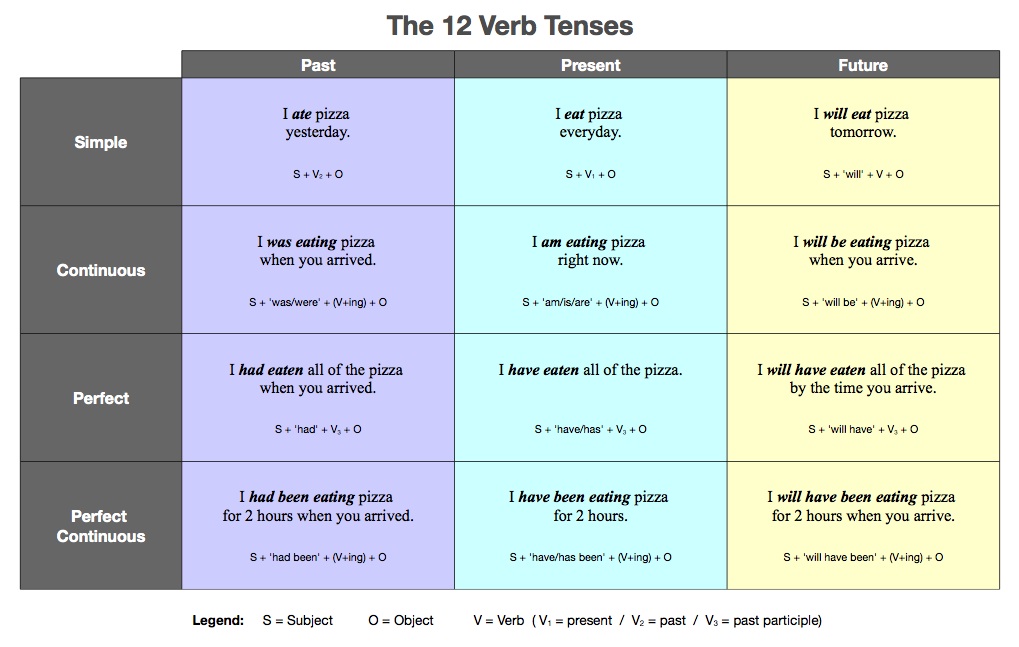
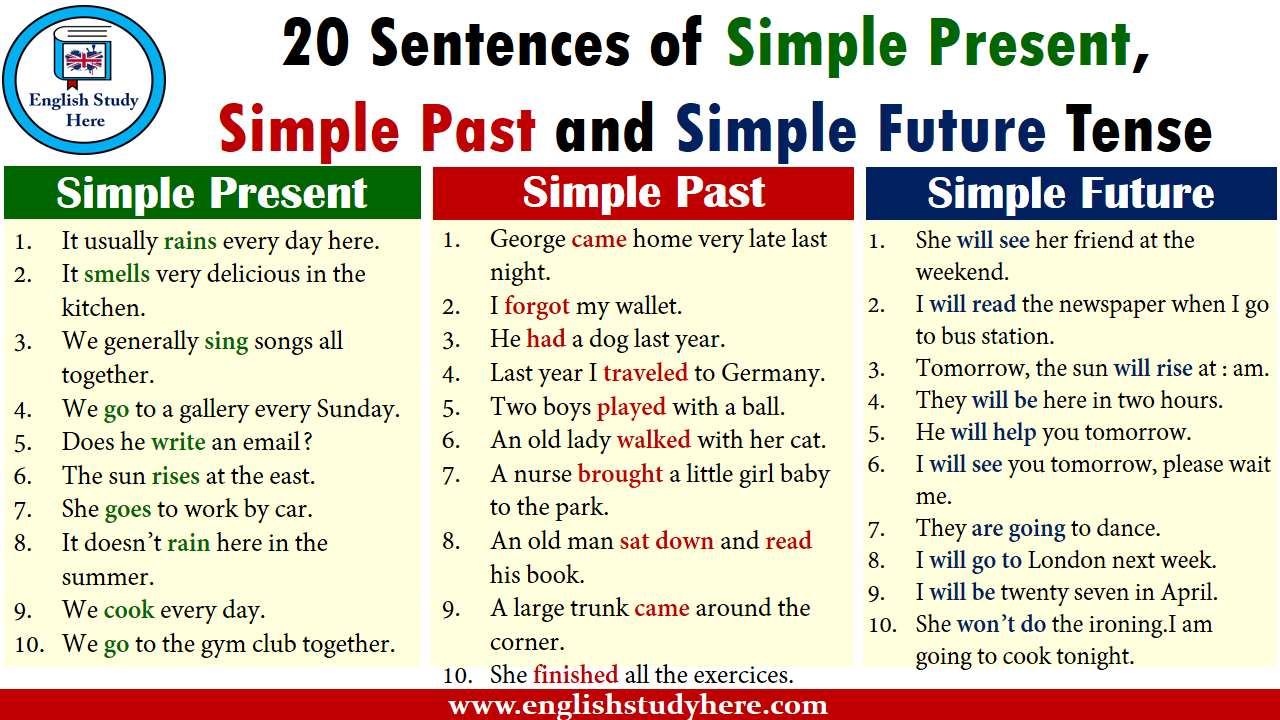
Simple Present Tense
I give, You give, He gives, We give, They give
Present Continuous Tense
• I am giving, You are giving, He is giving, We are giving,
They are giving.
Present Perfect Tense
I have given, You have given, He has given, We have given,
They have given
Simple Past Tense
I gave, You gave, He
gave, We gave, They gave.
Past Perfect Tense
• I had given• You had given• He had given• We had given•
They had given
Simple Future Tense
I shall/will give,
You will give, He will give, We shall/will give, They will give.
Future Perfect Tense
I shall/will have given,
You will have given, He will have given, We shall/will have given
They will have given.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
• I have been giving. You have been giving• He has been
giving
• We have been giving • They have been giving
Past Continuous Tense
I was giving, You were giving, He was giving We were giving,
They were giving.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
I had been giving, You had been giving , He had been giving
,We had been giving, They had been giving
Future Continuous Tense
• I shall/will be giving
• You will be giving • He will be
giving • We shall/will be giving • They will be giving
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
I shall/will have been giving ,You will have been
giving He will have been giving
He shall/will have been giving They will have been giving
Exercise in Grammar
Point out the Verbs in the following sentences and name
their tenses:-
1. The river flows under the
bridge.
2. I shall answer the letter to-night.
3. 1 knew he was there, for I had seen him come.
4. It has been raining all night.
5. I hear he has passed all right.
6. I had finished when he came.
7. He takes but little pride in his work.
8. I have been living here for months.
9. Be good, sweet maid.
10. By this time to-morrow I shall have reached my
home.
11. It is time we left.
12. He told me that he had finished
13. God forgive you !
14. He is waiting for you in the compound.
15. Piper, pipe that song again.
16. I am hoping to get a holiday soon.
17. Perhaps it were better to obey him.
18. Do noble deeds, not dream them all the day.
19. I shall have plenty of time tomorrow.
20. Though this be madness, yet there is method in it.
21. The king had never before led his troops in battle.
22. If he was guilty, his punishment was too light.
23. We have heard a strange story.