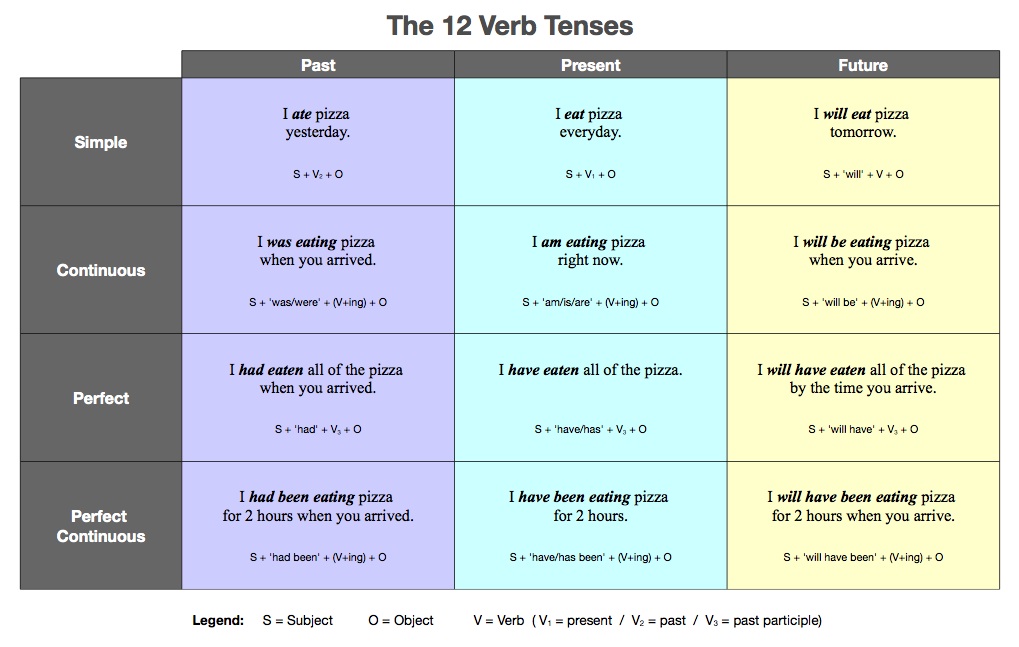
We all know that for every human, there is always a
composure of body parts in exception that are naturally or accidentally
omitted. The combinations of two letters or more make a word while the
combinations of two or more words make a sentence.
As our body consist
of various parts; so also the speech we utter constitute various parts. This is
why we called it parts of speech.
The parts of speech in English consist of 8. Which are:
Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjectives, preposition,
conjunction, interjection.
Hope you understand that? Now we shall pick them one after
the other for further explanation. Let's start with a Noun.

Definition of Noun
Consider the following picked words in the below sentences.
1. Olu is my friend. (Here olu is picked)
2. I was born and brought up in Lagos = Lagos
3. The goat is a domestic animal. = Goat
4. My Father has a big house in the village. = father, house, village.
5. Beauty is in the eyes of the beholder. = Beauty
From the words picked out from each of the sentence
above, a Noun can simply be defined as
word used to name people or person,
animals, places, things, ideas, emotions,
and so on.
When we say THINGS in the definition of Noun, it also
include what we can use the 5 senses for.
Secondly, it can mean what we can think of but cannot be
perceived by the senses.
Noun and its kinds
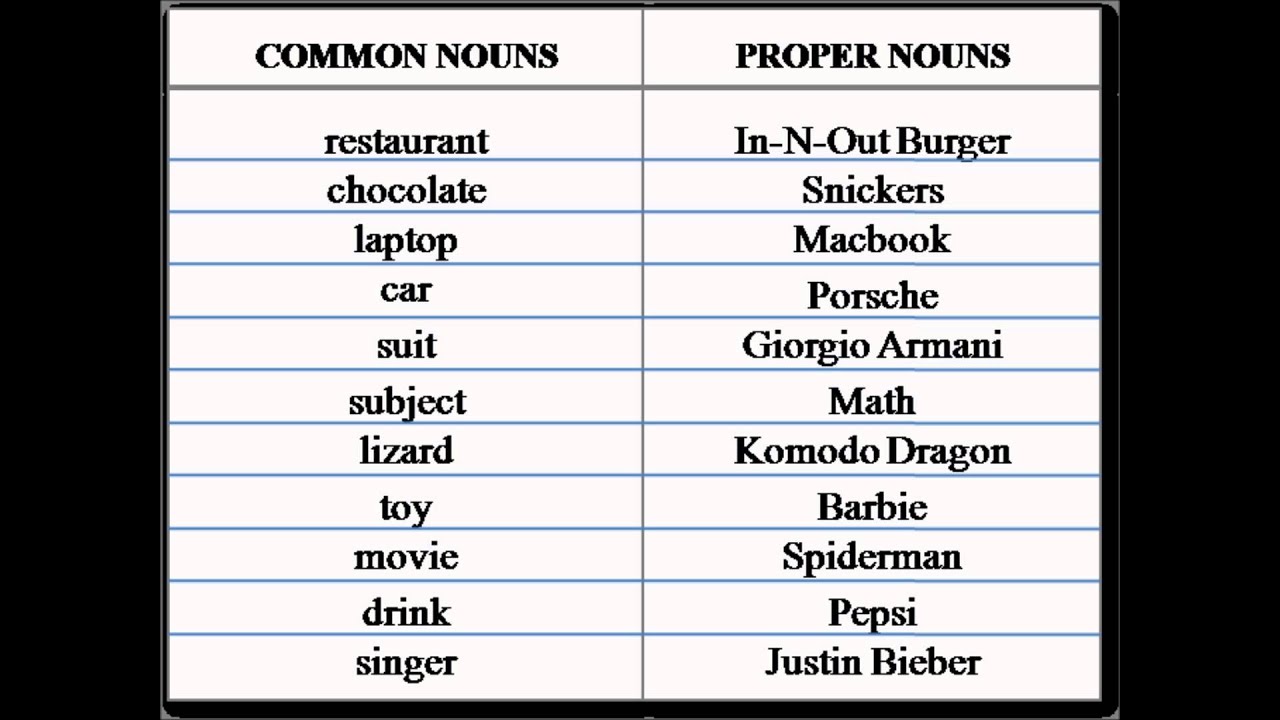
Common Noun: it is a general name of things, concept, ideas, animals and so on. In a
nutshell, it is a noun shared by all.
Such as the word girl, (we all know any
female living organism associated to humans with underdeveloped age is called
this), principal, town,
hotel, school and so on.
More so, it is a noun
of non specific i.e. if i should tell you to call me a girl in your classroom;
you can just go there and call any girl because i did not specify any girl.
Proper Noun: This refers to the specific names of :
A. Person: Tunde,
Funke, Adeola.
B. Cities,
towns, countries, continents, institutions and so on:
Lagos, Agege, World bank of Africa e.t.c
.
C. Months and days: January,
March, Monday.
N. B you will observe that each name under proper noun starts
with capital letter, , this
differentiate it from common Nouns. But note that a common noun needs not begin
with a capital letter unless it begins a sentence. Also every proper noun must
begin with a capital letter even if it occurs within a sentence. Examples:
1. Ade met Shola in the zoo.
2. Sheraton hotel is located in Maryland.
3. We went to the village in February.

Collective Noun: This is a noun used to refer to a group of
things or a class of individuals. Examples:
1. The herd of cattle is passing
2. A bunch of plantains,
keys.
3. A flock of sheep.
4. A team of players. Other words under collective Nouns
include swam(of bees) fleet of (cars) class of (students) and so on.
Abstract nouns: are things or concept that cannot be touched
or seen; they exist in our imagination. They also exist by experience and
feeling (emotion). Such of these nouns are, beauty, hatred, love, idea, death,
and so on.
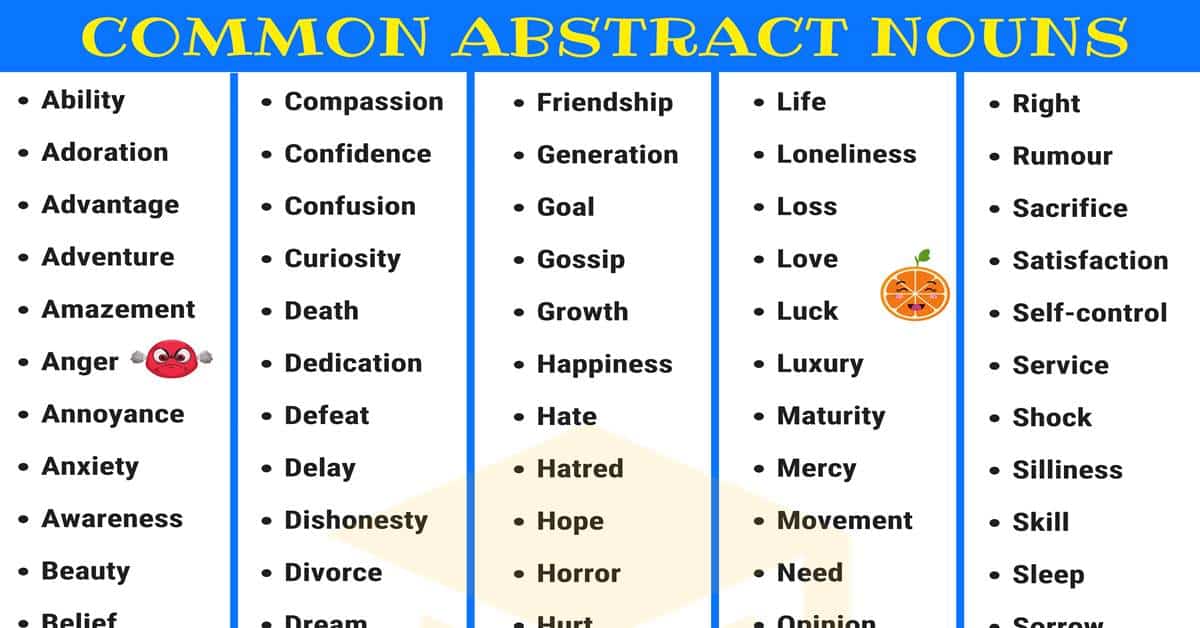
An Abstract Noun is usually the name of a quality, action,
or state considered apart from the
object to which it belongs; as.
Quality - Goodness, kindness, whiteness, darkness, hardness,
brightness, honesty, wisdom, bravery.
Action - Laughter, theft, movement, judgment, hatred.
State - Childhood, boyhood, youth, slavery, sleep, sickness,
death, poverty.
The names of the Arts and Science (e.g., grammar, music,
chemistry, etc.) are also Abstract
Nouns.
[We can speak of a brave soldier, a strong man, a beautiful
flower. But we can also think of these
qualities apart from any particular person or thing, and speak of bravery, strength, beauty by themselves. So also we
can speak of what persons do or feel apart
from the persons themselves, and give it a name. The word abstract means
drawn off.]
Abstract Nouns are formed:
(1) From Adjectives; as,
Kindness from kind; honesty from honest.
[Most abstract nouns are formed thus.]
(2) From Verbs: as,
Obedience from obey; growth from grow.
(3) From Common Nouns; as,
Childhood from child; slavery from slave.
Concrete Noun: All other types ofNoun ( common, proper and collective) except abstract nouns
are concrete nouns because they can be seen touched.
Another classification of nouns is whether they are
“countable” or “uncountable”. Countable
nouns (or countables) are the names of objects, people, etc. that we can
count, e.g., book, pen, apple, boy,
sister, doctor, horse.
Uncountable nouns (or uncountables) are the names of things
which we cannot count, e.g., milk, oil,
sugar, gold, honesty. They mainly denote substances and abstract things.
Countable nouns have plural forms while uncountable nouns do
not. For example, we say “books” but we
cannot say "milks"
We shall continue in our subsequent post. Kindly attempt
these questions.
Exercise 1
Point out the Nouns in the following sentences, and say
whether they are Common, Proper,
Collective or Abstract:
1. The crowd was very big.
2. Always speak the truth.
3. We all love honesty.
4. Our class consists of twenty pupils.
5. The elephant has great strength.
6. Solomon was famous for his wisdom.
7. Cleanliness is next to godliness.
8. We saw a fleet of ships in the harbour.
9. The class is studying grammar.
10. The Godavary overflows its banks every year.
11. A committee of five was appointed.
12. Jawaharlal Nehru was the first Prime Minister of India.
13. The soldiers were rewarded for their bravery.
14.Without health there is no happiness.
15. He gave me a bunch of grapes.
16. I recognized your voice at once.
17. Our team is better than theirs.
18. Never tell a lie.
19. Wisdom is better than strength.
20. He sets a high value on his time.
21. I believe in his innocence.
22. This room is thirty feet in length.
23. I often think of the happy days of childhood.
24. The streets of some of our cities are noted for their
crookedness.
25. What is your verdict, gentlemen of the jury?
Exercise 2
Write the Collective Nouns used to describe a number of
(1) Cattle;
(2) Soldiers;
(3) Sailors.
Write the qualities that belong to boys who are
(1) Lazy;
(2) Cruel;
(3) Brave;
(4) Foolish.
Exercise 3
Form Abstract Nouns from the following Adjectives:
Long,
young,
humble,
decent,
cruel,
bitter,
strong,
true,
short,
prudent,
dark,
deep,
wide,
wise,
good,
vacant,


/sample-letter-format-2063479-Final-dc968bbbf3ee4716a4a3875763fd4b09.png)